Listen to the blog by clicking below.
Nuleosome
A nucleosome is a section of DNA that is wrapped around a core of proteins. Inside the nucleus, DNA forms a complex with proteins called chromatin, which allows the DNA to be condensed into a smaller volume. When the chromatin is extended and viewed under a microscope, the structure resembles beads on a string. Each of these tiny beads is a called a nucleosome and has a diameter of approximately 11 nm. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. The chain of nucleosomes is then compacted further and forms a highly organized complex of DNA and protein called a chromosome.
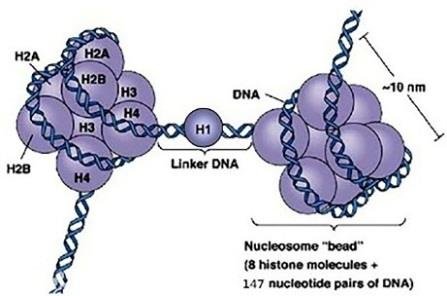

Chromatin



Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Nuclear DNA does not appear in free linear strands; it is highly condensed and wrapped around nuclear proteins in order to fit inside the nucleus.
Chromatin exists in two forms. One form, called euchromatin, is less condensed and can be transcribed. The second form, called heterochromatin, is highly condensed and is typically not transcribed.
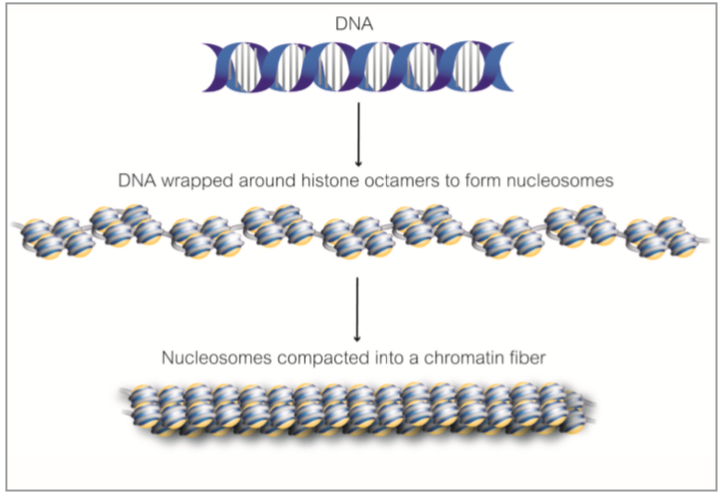
Under the microscope in its extended form, chromatin looks like beads on a string. The beads are called nucleosomes. Each nucleosome is composed of DNA wrapped around eight proteins called histones. The nucleosomes are then wrapped into a 30 nm spiral called a solenoid, where additional histone proteins support the chromatin structure. During cell division, the structure of the chromatin and chromosomes are visible under a light microscope, and they change in shape as the DNA is duplicated and separated into two cells.
크로마틴은 히스톤(histone)과 DNA로 구성된다: 147 bp DNA 체인이 8개의 core 히스톤 주변을 싸고 있는 것이 기초적인 크로마틴 유닛을 형성하고 이것을 뉴클레오솜이라고 부른다. 크로마틴의 주요한 기능들은 DNA를 세포에서 잘 맞게 더욱 작은 부피로 싸는 것을 하고, DNA가 mitosis(체세포 분열)과 meiosis(감수 분열)을 할 수 있도록 더욱 강화시킨다. 그리고 염색체(chromosome)가 부서지는 것을 막는다.
유전자 발현을 조절
DNA 복제를 조절
포유류의 경우, 크로마틴은 주요하게 집약되고, 발현적으로 silent 한 형태인 hetero크로마틴으로써 발견된다. 이것은 telomere와 pericentric 지역들, 그리고 반복되는 서열들이 많은 지역들로 구성된다. Euchromatinis는 대신에 덜 꽉차 있다. 그리고 그것은 가장 능동적으로 발현되는 유전자들을 포함한다.
위의 그림에서는 DNA가 히스톤 단백질 주변을 싸고 있고, 이것은 크로모좀(염색체)를 형성한다: 이러한 것들은 차례로 연결되어 염색질 섬유가 된다.
거대한 양의 단백질들은 크로마틴 구조를 형성하는데 참여하고, 이러한 크로마틴 구조는 히스톤과 TF라고 부르는 다른 크로마틴 상호작용 단백질, DNA 수리 단백질을 포함한다. 복합체를 리모델링하는 크로마틴은 크로마틴 구조를 뉴클레오솜과 DNA 사이의 상호작용을 조절함으로써 바꿀 수 있는 능력이 있다. 이것들은 종종 번역 후에 히스톤에 변형을 줌으로써 얻어진다.
댓글